ABA Therapy for Picky Eaters
Discover how ABA therapy for picky eaters can aid children with autism in overcoming mealtime challenges.
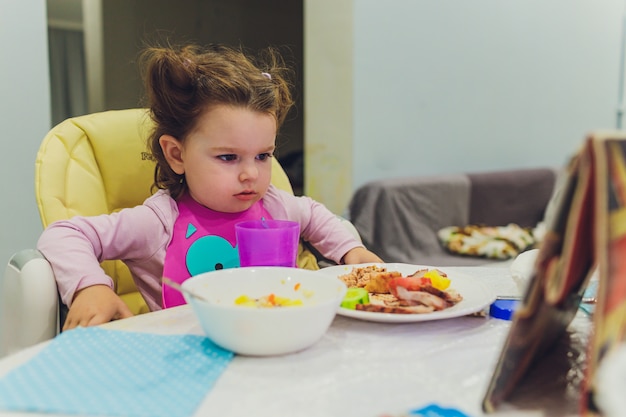

Understanding Picky Eating in Children
Picky eating in children, especially those with autism, can present significant challenges for families. Understanding the root causes and seeking professional guidance are critical steps in addressing these behaviors.
Identifying the Root Causes
Picky eating may stem from various factors. Behavioral causes can include sensory sensitivities, rigid routines, anxiety, and control issues. Children with autism are particularly vulnerable to these challenges, often leading to a heightened correlation between autism and picky eating Achieving Stars Therapy.
Before embarking on any behavioral intervention, it's essential to rule out other possible causes that may contribute to picky eating. These can include difficulties with chewing and swallowing, physiological issues such as sickness or allergies, or other medical concerns How to ABA. Consulting with speech-language pathologists (SLPs) or occupational therapists (OTs) who specialize in feeding issues is advisable in these cases.
| Possible Causes of Picky Eating | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensory Sensitivities | Increased sensitivity to textures, tastes, or smells of food. |
| Rigid Routines | Preference for specific routines that may limit food variety. |
| Anxiety | Stress during mealtimes affecting willingness to try new foods. |
| Physiological Issues | Medical conditions affecting chewing, swallowing, or allergies. |
Consulting with Professionals
Involving professionals such as psychologists, SLPs, and OTs can provide valuable insights into a child's picky eating habits. These specialists can help identify specific challenges and develop targeted interventions designed to promote healthier eating behaviors. A structured approach to expanding a child's food repertoire is essential. This often involves starting with small approximations of new foods and gradually increasing exposure through a carefully planned hierarchy of foods Achieving Stars Therapy.
Establishing consistent mealtime routines and creating a supportive environment can also positively impact a child's eating habits. Visual supports, such as picture schedules, gradual food introductions, and modeling good mealtime behavior, are effective strategies for parents to implement at home Achieving Stars Therapy. Combining these approaches with behavioral interventions can lead to significant progress in overcoming picky eating challenges.
ABA Therapy for Picky Eaters
Importance of Socially Significant Goals
In ABA therapy, setting socially significant goals is essential for fostering meaningful changes in children's eating behaviors. These goals are tailored to meet the specific needs of each child, focusing on expanding their food preferences and overall dietary variety. The U.S. Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association endorse ABA therapy as an effective treatment approach, particularly for children with autism who face challenges with picky eating Magnet ABA.
One of the key aspects of setting these goals involves identifying which foods are most critical for nutritional balance. Progress is typically measured through data collection, highlighting improvements in food acceptance and reduction of aversive reactions to new foods.
Structured Approach in ABA Therapy
ABA therapy employs a structured approach that gradually introduces new foods to children. This method uses techniques such as reinforcement and positive encouragement to motivate children to try and accept a wider variety of foods. Studies show that through approximately 100 therapy sessions, children have transitioned from consuming as few as four food options to over 50 different choices Cross River Therapy.
The structured nature of ABA therapy includes:
- Assessment: Evaluating the child's current eating habits and food preferences.
- Goal Setting: Establishing personalized objectives that are relevant and achievable.
- Intervention: Implementing various strategies to introduce new foods in a supportive manner.
- Monitoring Progress: Collecting data on food acceptance to track improvements over time.
This systematic approach ensures that children's unique needs are met, making it an effective resource for combating picky eating.
Success Stories with ABA Therapy
Numerous success stories highlight the benefits of ABA therapy for picky eaters, specifically among children with autism. Reports indicate that participants in ABA programs have significantly increased their food acceptance, moving from consuming less than 15 foods to over 50 options Cross River Therapy. These transformations not only enhance the child's diet but also positively impact their overall quality of life.
Parents have expressed gratitude for the support and guidance provided by ABA therapists, noting improvements in mealtime experiences and reduced anxiety around food. By focusing on achieving socially significant goals through a structured methodology, ABA therapy presents a promising solution for families struggling with picky eating issues. Parents seeking further information can explore the success rates of ABA therapy to understand its effectiveness more comprehensively.
Role of ABA Therapy in Autism
ABA therapy plays a crucial role in supporting children with autism, particularly in addressing their challenges with picky eating. This section will explore the endorsements from health authorities, the impact on children with autism, and how ABA therapy helps address mealtime challenges.
Endorsement by Health Authorities
The effectiveness of ABA therapy has gained recognition from various health authorities. Notably, the U.S. Surgeon General and the American Psychological Association endorse ABA therapy as a top-tier treatment for picky eating, especially in children with autism. These endorsements highlight the therapy's importance in improving eating habits and overall well-being among children who struggle with these issues [1].
Impact on Children with Autism
Numerous studies and real-world applications demonstrate the significant impact of ABA therapy on the diets of children with autism. The therapy employs evidence-based techniques that target and modify behaviors, helping these children expand their food preferences and improve their eating habits. Children undergoing ABA programs have shown remarkable improvements, such as consuming at least 30 bites of all food items offered during meals or successfully trying up to seven different nonpreferred foods presented together [2].
| Improvement Aspect | ABA Program Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Bites of All Foods Offered | Average of 30 |
| Different Nonpreferred Foods | Successfully consuming up to 7 |
Addressing Mealtime Challenges
Mealtime can present unique challenges for children with autism. ABA therapy addresses these obstacles by incorporating structured interventions that create a more positive dining experience. By using reinforcement strategies and teaching new skills, ABA practitioners help children overcome their aversions to certain foods and build healthier eating habits. The method also emphasizes family involvement, providing guidance to parents on how they can support their children's mealtime endeavors [3].
Furthermore, ABA techniques help children learn to manage their emotions and behavior around food, thus improving their overall relationship with eating. Parents seeking to understand the broader applications of ABA, including its collaborations with other therapies, can refer to related areas such as aba therapy and occupational therapy integration and aba therapy and self-help skills.
Through consistent application of ABA therapy, families can witness substantial changes in their children's eating behaviors, leading to healthier diets and enhanced quality of life.
Behavioral Approaches vs. Responsive Feeding Therapy
Parents exploring options for addressing picky eating in their children often encounter two primary methods: behavioral approaches, commonly used in ABA Therapy for Picky Eaters, and responsive feeding therapy. Each method has distinct strategies and philosophies that cater to diverse needs.
Utilizing Rewards and Consequences
Behavioral approaches, as employed in ABA therapy, are centered around using rewards and consequences to encourage positive eating behaviors. This method often includes implementing specific interventions, such as using social praise, other reinforcers, and token systems when the child eats a predetermined number of bites of non-preferred foods within a set timeframe [4].
One example of a structured intervention might look like this:
| Goal | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Increase food acceptance | Use of social praise and token systems | Child increases food variety |
| Gradual exposure | Gradual introduction of new foods | Acceptance from 4 to over 50 different foods |
Techniques such as hand-over-hand guidance have shown effectiveness, with participants improving their food acceptance significantly [2].
Emphasizing Autonomy in Mealtimes
In contrast to behavioral approaches, responsive feeding therapy emphasizes respecting the child's autonomy during mealtimes. This method creates a comfortable and stress-free environment, allowing the child to take the lead in meal choices without pressure. By building trust, caregivers reduce mealtime anxiety and cultivate a more positive relationship with food [5].
Responsive feeding techniques are beneficial in creating an encouraging atmosphere, allowing children to explore different foods at their own pace. This approach may foster a sense of independence and comfort that encourages gradual acceptance of a wider variety of foods without the pressure of immediate compliance.
Overall, the choice between behavioral approaches and responsive feeding therapy depends on the unique needs of the child and family. Understanding these methodologies allows parents to make informed decisions about which strategy may work best to foster healthy eating habits in their children. For more insights on how ABA techniques can help, visit our section on aba therapy for cognitive skills development.
ABA Techniques for Expanding Food Choices
To effectively address picky eating in children, particularly those with autism, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy employs various techniques. Two significant aspects of this approach are data-driven progress tracking and the development of customized treatment plans.
Data-Driven Progress Tracking
A structured approach in ABA therapy includes meticulous tracking of a child's eating habits. This involves maintaining a food log to analyze patterns and reactions to different foods. A hierarchy of acceptable foods is established to categorize items based on the child's willingness to try them. New foods are introduced gradually, starting with small portions, and progress is monitored through data collection.
Using a rating scale, therapists can assess tolerances and the child's acceptance of various foods. This quantitative data allows for a clear picture of improvement over time and helps inform future strategies. For example, children often show a marked increase in food acceptance, moving from less than 15 to over 50 different foods by implementing such techniques.
| Food Acceptance Levels | Before Therapy | After Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Foods Tried | <15 | >50 |
| Frequency of Meal Disruption | High | Low |
This method not only encourages accountability but also allows for adjustments in the plan based on the child's responses.
Customized Treatment Plans
One of the key strengths of ABA therapy is the ability to customize treatment plans tailored to each child's unique needs. Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) are responsible for designing these individualized programs based on the child’s skills, interests, and family dynamics. The customization ensures that the strategies used are effective in addressing the specific picky eating behaviors of the child.
These plans focus on various aspects, including the child’s current preferences and any aversions they may have. By adopting a flexible approach, caregivers can engage children in ways that resonate with their interests, thereby increasing motivation to try new foods. Family involvement is also emphasized in ABA programs, enhancing the support system surrounding the child's eating habits [3].
Overall, both data-driven tracking and customizable strategies are essential components of ABA therapy for picky eaters, ensuring that children receive the best possible care while expanding their food choices in a supportive environment.
Research Studies and Success Stories
The effectiveness of ABA therapy in addressing picky eating, particularly in children with autism, has been supported by various research studies and success stories. This section highlights key statistics, real-life impacts of ABA interventions, and specific case studies that showcase the effectiveness of ABA therapy for picky eaters.
Stats on Autism and Picky Eating
Research indicates that nearly 70% of children with autism exhibit abnormal eating behaviors, which is significantly higher than that of neurotypical peers in the same age group [1]. This insistence on certain foods or refusal to try new items can severely limit their nutrition and overall eating experience.
In a notable study, it has been observed that after approximately 100 sessions of ABA therapy, children can transition from consuming just 4 different foods to over 50 distinct food options. Such transformations illustrate the potential impact of structured interventions on expanding a child's food repertoire.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Percentage of autistic children with abnormal eating behaviors | 70% |
| Average number of food items consumed before ABA therapy | 4 |
| Average number of food items consumed after 100 sessions | 50+ |
Real-Life Impacts of ABA Interventions
Parents often report significant improvements in their children’s willingness to try new foods and their overall eating habits following ABA therapy interventions. Behavioral procedures such as differential reinforcement of alternative behavior, escape extinction, and stimulus fading have been found effective in increasing food acceptance among picky eaters including those on the autism spectrum [4].
A structured approach to addressing picky eating through ABA therapy is not just about increasing food variety; it is focused on creating a supportive environment that encourages gradual acceptance. For instance, keeping a food log can help analyze eating patterns and establish a hierarchy of acceptable foods, starting with small, non-threatening food items.
Case Studies and Intervention Effectiveness
Numerous case studies validate the effectiveness of ABA therapy for children struggling with food acceptance. One such case highlighted a young child who demonstrated extreme selectivity in food choices. Through a combination of data-driven progress tracking and a tailored treatment plan, the child was empowered to try new foods systematically, resulting in increased food variety at mealtimes.
Feedback from parents underscores the importance of combining ABA techniques with family involvement, creating an environment that prioritizes both behavioral change and emotional security. For further insights into how family dynamics intersect with therapy, see our article on aba therapy and family involvement.
The growing body of research and success stories indicates that ABA therapy does not merely address the symptoms of picky eating in children with autism, but provides effective strategies to foster healthier eating habits and improve their overall quality of life.
References
Find More Articles
Contact us
North Carolina, Tennessee, Nevada, New Jersey, Utah, Virginia
New Hampshire, Maine
Massachusetts, Indiana, Arizona, Georgia
.avif)







































.jpeg)