How ABA Therapy Helps Children Build Friendships and Connections
Unlocking Social Potential: The Impact of ABA Therapy on Children with Autism

Introduction
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy has emerged as a cornerstone in supporting children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in developing social skills that are crucial for forming friendships and meaningful connections. Through a structured and individualized approach, ABA therapy offers various techniques that help children overcome communication barriers and navigate social complexities. This article explores the comprehensive ways in which ABA therapy aids children with autism in building lasting relationships.
Understanding ABA Therapy: A Foundation for Social Skills

Overview of ABA Therapy
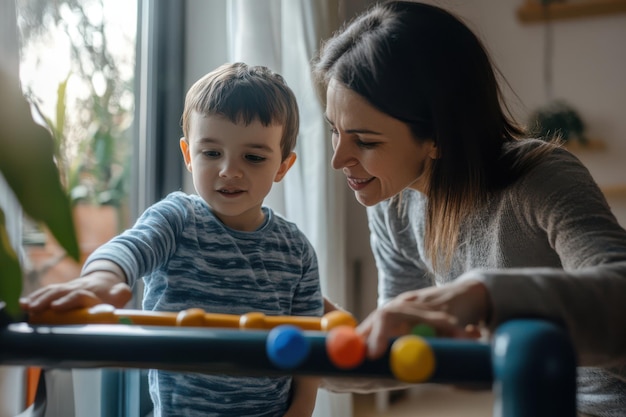
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a structured, research-based approach aimed at improving specific behaviors through systematic intervention strategies. It creates positive changes in crucial areas like communication, self-care, and, importantly, social skills for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). By assessing individual needs, therapists can craft personalized plans that focus on breaking down complex social interactions into manageable parts.
Importance for Children with ASD
For children with ASD, developing social skills is a vital aspect that influences their ability to form friendships and connect with others. ABA therapy supports this objective by using techniques such as role-playing, modeling, and positive reinforcement. By teaching skills like making eye contact, greeting others, and understanding social cues, ABA therapy helps children gain the confidence needed to engage effectively in social situations. The generalization of these skills across different contexts empowers them to apply what they learn successfully in schools, homes, and community settings.
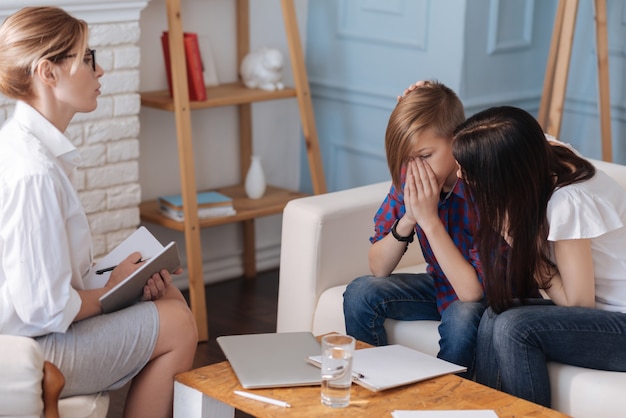
Initial Assessment and Tailored Interventions
The journey begins with a thorough assessment conducted by Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) to identify each child's strengths and weaknesses. This initial step is crucial for designing interventions that are not only effective but also resonate with the unique needs of the child. The following components are part of creating tailored interventions:
- Behavioral Assessments: Evaluating communication difficulties and social skill deficits.
- Individualized Goals: Setting specific objectives based on the child’s circumstances.
- Parental Involvement: Training caregivers to reinforce new skills at home, ensuring consistency and encouragement.
How Does ABA Therapy Assist in Skill Development?
ABA therapy assists in the development of various skills for individuals with autism by employing evidence-based techniques tailored to each individual's unique needs. It enhances language and communication, social skills, memory, attention, and daily living skills while minimizing harmful behaviors. Through strategies like positive reinforcement, ABA encourages the repetition of desired behaviors, making learning more effective. Additionally, therapists conduct functional behavior assessments to understand the triggers for challenging behaviors, allowing for targeted interventions. By focusing on real-life applications and involving parents in the process, ABA therapy supports individuals in integrating learned skills into their daily lives, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Enhancing Communication Skills Through ABA

How does ABA therapy help improve communication skills in children with autism?
ABA therapy employs a comprehensive approach to bolster communication skills in children with autism. By using evidence-based techniques, it enhances both expressive and receptive language capabilities. Children learn to expand their vocabulary and understand sentence structures through various resources such as visual aids and play-based therapy.
Role of verbal and non-verbal techniques
Therapists emphasize activities that teach not only verbal communication but also non-verbal techniques. These include role-playing exercises where children practice initiating conversations and utilizing appropriate body language, such as maintaining eye contact and using gestures. Techniques like Discrete Trial Training (DTT) break down language skills into manageable parts, thereby making it easier for children to grasp complex concepts and apply them in real-life scenarios.
Impact on social interactions
The positive repercussions of improved communication extend into social interactions as well. Children are better equipped to engage with peers and caregivers, leading to enriched relationships. By understanding social cues and learning to express their needs effectively, children experience enhanced self-esteem and increased peer support. Overall, ABA therapy significantly contributes to a child's ability to form meaningful connections, promoting an inclusive environment that fosters friendship and mutual understanding.
| Skill Area | ABA Techniques Involved | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Expressive Language Skills | Play-based learning, DTT | Expanded vocabulary and sentence structure |
| Non-verbal Communication | Role-playing, modeling | Improved eye contact and body language |
| Social Engagement | Peer-mediated activities | Enhanced ability to form friendships |
Teaching Empathy and Understanding Emotions

Empathy Activities in ABA
Empathy is an essential component of social skills, particularly for individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). ABA therapy often includes specific activities designed to cultivate empathy. For example, therapists might use perspective-taking exercises where children are encouraged to consider how others feel in certain situations. This helps them to recognize different emotions and respond appropriately.
Responding to Emotions
Understanding how to respond to others' emotions is crucial for building relationships. ABA therapy employs strategies that teach children to identify emotional cues through activities such as emotion charades or using visual aids like emotion cards. By practicing these skills, children learn to react in socially appropriate ways, which fosters deeper connections with peers and caregivers.
Role-Playing Techniques
Role-playing is a powerful tool in ABA therapy. It allows children to explore various social scenarios in a safe environment. During role-playing sessions, children can practice initiating conversations, interpreting social cues, and expressing their feelings. This hands-on experience builds confidence and equips them with the skills necessary to engage effectively with others in real-life situations.
| Technique | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Perspective-Taking | Activities to consider others' feelings | Enhances empathy |
| Emotion Identification | Using tools like emotion cards | Improves response to emotions |
| Role-Playing | Practicing social interactions in scenarios | Builds confidence and skills |
Through these strategies, ABA therapy plays a pivotal role in teaching empathy, helping children understand and navigate emotional landscapes in social settings.
Unlocking Social Interaction Through Structured Learning
What are the benefits of ABA therapy for enhancing social skills in children with autism?
ABA therapy is a comprehensive and research-backed approach that brings numerous benefits for enhancing social skills in children with autism. It employs structured methods, including role-playing and positive reinforcement, to foster a supportive learning environment that encourages communication and interaction.
Role-Playing Scenarios
Role-playing provides children the opportunity to practice social situations in a safe, controlled environment. By mimicking interactions, children learn to initiate conversations, maintain eye contact, and take turns in discussions—essential skills for engaging effectively with peers. This technique allows them to rehearse responses and to gain confidence in real-world settings.Social Stories and Peer Interactions
Social stories are valuable tools that present narratives about various social situations and appropriate behaviors. They help clarify social expectations and responses. Alongside peer-mediated interventions, where typically developing peers encourage social skill usage, these methods strengthen friendships and introduce children to social networks that foster their development.Developing Essential Social Skills
ABA therapy enhances crucial social skills by implementing targeted strategies. Children learn to greet others, interpret social cues, and respond with empathy during interactions. Group activities further this learning, providing opportunities for building relationships, sharing experiences, and enhancing their overall social competence.
Through these structured interventions, ABA therapy promotes essential life skills that significantly improve social interactions and the quality of relationships for children with autism.
Managing Behaviors for Positive Social Outcomes
Addressing Problem Behaviors
ABA therapy plays a significant role in understanding and managing problem behaviors that may obstruct social interactions. By identifying specific triggers, therapists can develop strategies that help individuals learn appropriate responses. This management fosters a more positive and engaging social environment for both the children and those around them.
Reinforcement Strategies
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone of ABA therapy, effectively motivating children to repeat desirable social behaviors. By rewarding actions like raising hands in class or sharing with peers, children gain confidence and practice social skills in an enjoyable manner. These affirmative strategies drive engagement and enhance the likelihood that these behaviors will become routine.
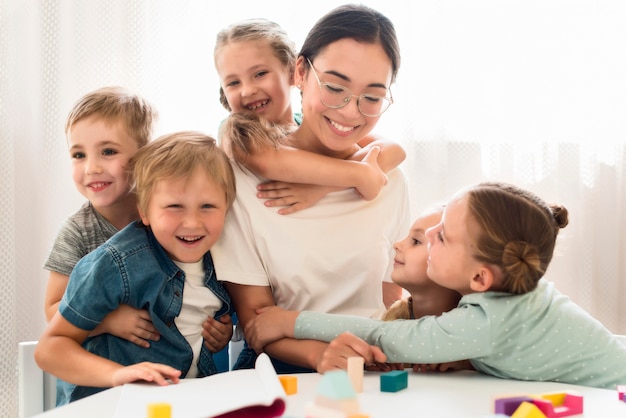
Creating Supportive Social Environments
A nurturing social environment is essential for children with autism to thrive. Group sessions provide opportunities for direct interaction, allowing individuals to practice social skills in real-life contexts. Such inclusive settings not only help in forming friendships but also support emotional connections, enabling children to feel accepted and valued. By promoting peer relationships and fostering a sense of community, ABA therapy contributes significantly to the development of strong social skills.
Parent and Caregiver Involvement: Extending Learning Beyond Therapy

How can parents support their children in applying ABA therapy social skills in everyday situations?
Parents play a crucial role in reinforcing the skills learned during ABA therapy. One effective way to do this is by creating real-life opportunities for social interaction. Arranging playdates, group activities, or community events can help children practice their skills in a natural setting, improving their confidence and social competence.
Another strategy is modeling appropriate social behaviors themselves. Parents can demonstrate how to greet others, maintain eye contact, or share during conversations, allowing children to observe and learn. Using visual aids, such as social stories, can clarify expectations and reinforce the lessons learned in therapy.
Collaboration with Educators
Consistent communication and collaboration with educators are vital. By aligning strategies used at home and school, parents help ensure that their child’s learning environment supports skill generalization. This collaboration allows children to experience a cohesive approach, which can enhance their ability to transfer skills learned in therapy to different contexts.
Emotional support and positive reinforcement are equally important. When parents celebrate successes, no matter how small, and offer encouragement, children feel more motivated to engage socially. Monitoring progress and adapting interventions based on their child's needs can further tailor the learning experience, ensuring that it remains effective and relevant.
Overall, an involved and supportive parent or caregiver can significantly enhance the effectiveness of ABA therapy in social skill development.
Practical Applications: From Therapy to Everyday Success

Generalization of Skills
ABA therapy emphasizes the importance of generalizing learned social skills to various environments. Techniques such as Natural Environment Training (NET) allow children to practice in everyday settings, enhancing their ability to adapt learned behaviors to real-life situations. This approach encourages skills such as initiating conversations and interpreting social cues to be used effectively outside therapy sessions.
Real-World Applications
Through structured activities, children learn foundational skills—like turn-taking or greeting others—that are crucial for interactions with peers, siblings, and caregivers. Group sessions within ABA therapy provide a platform for children to practice these skills in real time, fostering peer relationships and allowing them to engage more confidently in social situations.
Building Confidence and Independence
Positive reinforcement plays a vital role in ABA therapy, motivating children to repeat desired behaviors. Activities such as role-playing and modeling help build confidence, enabling children to navigate social interactions successfully. As they acquire essential skills, strong peer connections develop, significantly enhancing their self-esteem and overall independence.
Fostering Peer Support and Building Friendships
How are Peer-Mediated Interventions Used?
Peer-mediated interventions play a crucial role in enhancing social skills for children with autism. In this approach, typically developing peers are strategically included in therapeutic activities. These peer partners help reinforce social skills, encourage interactions, and provide models of appropriate behaviors. As a result, children with autism gain opportunities to form friendships and build their confidence in social situations.
What Role Do Group Activities Play in ABA Therapy?
Group activities are integral to ABA therapy, allowing children to engage in social interactions with their peers in a structured setting. These activities provide a safe space for practicing skills like turn-taking, sharing, and initiating conversations. Through peer interactions during these sessions, children develop stronger bonds and learn to navigate the complexities of social relationships.
How Can Supportive Peer Networks Be Built?
Creating supportive peer networks is essential for fostering friendships among children with autism. Programs that emphasize inclusivity can cultivate an environment where all children feel accepted and supported. By leveraging shared interests and promoting collaboration, children with autism can connect with peers, leading to enhanced social interactions and meaningful relationships. This support system is vital for their emotional and social development.
Conclusion
ABA therapy offers a comprehensive framework for children with autism to develop the necessary skills for forming friendships and building lasting connections. Its tailored approach ensures that each child can overcome social challenges, fostering an environment where communication and empathy thrive. With continued support from parents and caregivers and the integration of learned skills into everyday life, ABA therapy paves the way for sustainable social engagement and friendships, ultimately enriching the lives of children with autism.
References
- ABA Therapy for Social Skills: Building Connections
- How ABA Therapy Can Support Your Child's Development
- How ABA Therapy Helps Improve Social Skills in Children
- How ABA Therapy Enhances Social Skills in Children with ASD
- Fostering Friendships in Kids with Autism | ABA Therapy Near Me
- Benefits of ABA Therapy for Children with Autism
- Enhancing Communication Skills With ABA Therapy
- Common ABA Therapy Strategies for Children With Autism
- Enhancing Social Skills Through ABA Therapy
- Our Autism & ABA Therapy Services - Surpass Behavioral Health
Find More Articles
Contact us
North Carolina, Tennessee, Nevada, New Jersey, Utah, Virginia
New Hampshire, Maine
Massachusetts, Indiana, Arizona, Georgia
.avif)









%2520(1).jpeg)































.jpeg)









































.jpeg)







.jpeg)
.jpeg)