How School-Based ABA Therapy Helps Address Disruptive Classroom Behaviors
Harnessing School-Based ABA Therapy for Better Classroom Management

Understanding School-Based ABA Therapy
Overcoming classroom disruptions through effective behavioral interventions is critical for academic success, particularly for students who face challenges in traditional learning environments. School-based Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a systematic approach that offers educators and students the tools needed to enhance learning and social skills, reduce disruptive behaviors, and create a more conducive educational environment. This narrative explores the multifaceted benefits of ABA therapy, its application in schools, and its effectiveness in preparing students for successful academic and social experiences.
The Benefits of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy in Schools

What are the benefits of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in schools?
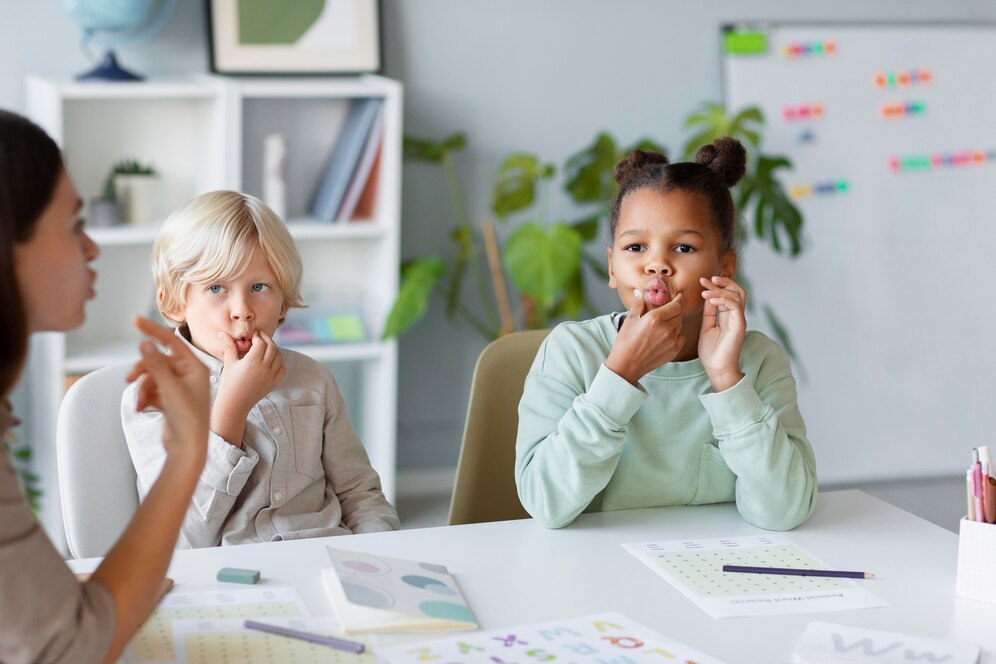
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy in schools offers numerous advantages that enhance both learning and social interactions among students. It is especially effective for diverse student populations, including those with autism and other behavioral challenges.
Improved Communication and Learning
ABA strategies focus on developing essential communication skills, leading to improved understanding of classroom instructions and better interactions with peers and teachers. Students learn through small, manageable tasks, reinforcing skills necessary for reading, writing, and math.
Enhanced Behavioral Management
ABA employs evidence-based strategies such as positive reinforcement and token economies to modify behavior. These methods not only promote compliance but also enhance self-regulation and independence among students.
A Structured Learning Environment
By establishing clear routines and consistent expectations, ABA therapy helps create a structured environment that minimizes classroom disruptions. This approach is vital for keeping students engaged and focused on their academic goals.
Versatility Across Diagnoses
Research supports ABA's effectiveness across various conditions, including ADHD and PTSD, demonstrating its comprehensive approach to behavioral intervention.
Overall, ABA plays a crucial role in fostering a conducive learning environment, making it invaluable in school settings.
Effectiveness of ABA Therapy in Reducing Disruptive Classroom Behaviors

How effective is ABA therapy in reducing disruptive classroom behaviors?
ABA therapy has proven to be highly effective in curbing disruptive classroom behaviors, especially among students diagnosed with autism. The core of ABA lies in using structured interventions that modify behaviors through reinforcement strategies. This process encourages desired behaviors while decoupling them from negative actions, such as aggression or noncompliance.
A critical component of successful ABA implementation is the Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA). The FBA identifies problematic behaviors and their underlying triggers, providing insights into how environmental factors contribute to disruptive actions. This allows educators and therapists to tailor specific interventions that meet each child's individual needs, enhancing overall effectiveness.
What role do Functional Behavior Assessments play in ABA?
The FBA serves as an essential tool for both educators and therapists in the ABA framework. By assessing the function of behaviors, it becomes possible to create interventions that not only manage the behaviors but also address their root causes. For instance, if a student displays disruptive behavior due to unmet needs, the intervention will aim to fulfill those needs, leading to a more engaged and compliant student.
Moreover, research emphasizes that consistent application of ABA interventions—combined with ongoing monitoring and adjustments—can significantly enhance communication and social skills. This not only improves individual behavior but also fosters a positive learning environment for all students.
In conclusion, ABA therapy's structured approach and focus on individualized strategies make it a prominent choice for managing disruptive behaviors, ultimately supporting a nurturing atmosphere conducive to learning.
ABA's Role in Educational Transition and Skill Development

What role does ABA play in educational transition services?
ABA plays a crucial role in educational transition services by utilizing individualized strategies to support students in developing essential academic and social skills. This is particularly effective for individuals on the autism spectrum and those facing behavioral challenges.
Contemporary ABA practices emphasize ethical and compassionate approaches that focus on positive reinforcement. Such methods encourage desired behaviors while promoting a nurturing environment for learning.
Additionally, ABA integrates emotional regulation strategies, addressing mental health needs alongside observable behaviors. This holistic approach ensures that students not only improve their academic capabilities but also learn important social skills.
Extensive research supports the efficacy of ABA. Programs are tailored through functional behavior assessments conducted by certified behavior analysts, ensuring that interventions are effective and responsive to individual needs. Key components include ongoing data collection and collaboration with families, making the transition process smoother and more effective.
Developing academic and social skills through ABA
School-based ABA therapy breaks down complex academic tasks into manageable steps, allowing students to focus better and complete assignments successfully. This method not only reduces classroom disruptions but also enhances learning.
Moreover, ABA strategies like token economies, discrete trial teaching, and naturalistic teaching engage students and promote positive behaviors. For instance, visual strategies, including token boards, can effectively engage students who respond better to visual cues than verbal instructions.
By fostering communication skills and understanding social cues, ABA prepares students for successful interactions in the classroom. This personalized approach helps develop self-regulation and independence—vital components for academic success.
Preparing Students for School with ABA Therapy

How does ABA therapy prepare students for school environments?
ABA therapy prepares students for school environments by focusing on essential skills needed for academic success and social interactions. One key aspect of this therapy is improving communication abilities. Children learn to express themselves clearly, which is vital for understanding instructions from teachers.
In addition, self-regulation and adaptability are fostered through individualized interventions, tailored specifically to meet each child's unique needs. Such customization ensures that every student receives appropriate support that aligns with their personal challenges, thereby allowing them to adapt more seamlessly to school settings.
ABA therapy also directly addresses challenging behaviors that can disrupt learning. By implementing targeted interventions, educators can help students manage their behaviors, which fosters better engagement in the classroom. Specific techniques, like breaking tasks into smaller, manageable parts, promote a greater focus on assignments and reduce instances of distraction.
How do individualized ABA interventions contribute to academic success?
Individualized ABA interventions play a crucial role in shaping a child's academic journey. By utilizing strategies such as
- Positive reinforcement for desired behaviors,
- Token economies for motivation, and
- Visual supports to enhance understanding, students can navigate the school day with increased confidence.
Moreover, interventions aim to develop social skills such as sharing, cooperation, and understanding social cues. These skills are essential for building friendships and participating in group activities, which in turn contribute to a more integrated school experience.
Overall, by implementing ABA therapy, children not only learn academically but also prepare socially for the challenges of school, allowing for a holistic approach to readiness.
Practical ABA Strategies for Educators

Implementation of ABA Techniques in Classroom Settings
Integrating Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) strategies into classroom environments offers significant benefits in managing student behavior. Educators can implement techniques such as clear routines, which establish expectations for students and allow multiple practice opportunities. This method directly addresses behavioral challenges by providing a structured setting that minimizes confusion and supports focus.
Strategies like using silent signals instead of verbal reprimands help discreetly manage behavior without interrupting the learning flow. Additionally, incorporating brain breaks can assist students, especially those with ADHD, by refreshing their attention and reducing burnout. For those prone to distraction, maintaining close physical proximity can subtly redirect their focus.
Effective use of visual strategies, including token boards, allows educators to engage students who respond better to visual cues. These approaches create an environment where positive behaviors are consistently reinforced, promoting an overall conducive classroom atmosphere.
Importance of Ongoing Professional Development
Ongoing professional development in ABA techniques is vital for educators to stay effective in managing classroom behaviors. Regular training ensures that teachers are equipped with the latest strategies to meet the diverse needs of their students. Studies show that when educators receive robust ABA training, they are better prepared to implement techniques that foster a positive learning environment.
Training also helps address misconceptions about ABA, such as the idea that reinforcement is the same as bribery. Educators need to understand that reinforcement is a vital part of promoting desired behaviors effectively. Moreover, administrative support in implementing ABA methods is crucial, ensuring teachers have access to necessary resources and continued learning opportunities to enhance their skills and effectiveness in minimizing classroom disruptions.
Challenges and Success Stories in ABA Implementation
Overcoming Challenges in ABA Application
Implementing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in school settings poses several challenges. Reports indicate that nearly a third of public school teachers feel student misbehavior significantly impacts their teaching. Consequently, equipping educators with the necessary ABA training is vital but often inadequate due to limited resources and misunderstanding of the techniques. For instance, there is a common misconception that reinforcement methods resemble bribery, which can deter educators from using effective strategies.
Moreover, the importance of implementation fidelity cannot be overstated. Effective ABA strategies hinge on principles of behavior modification that require consistent application. When these strategies lack fidelity, it can result in heightened disruptions instead of managing them.
Success Stories of ABA in Education
Despite the challenges, numerous success stories showcase the positive impact of ABA therapy in educational environments. A growing number of schools that incorporate ABA techniques report improved student behavior and enhanced learning outcomes. For example, implementing clear routines and positive reinforcement strategies leads to meaningful reductions in classroom disruptions, thereby fostering a more conducive learning atmosphere for all students.
Schools have also seen improvements in students with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) as individual support through ABA therapy enhances their social skills, communication abilities, and overall academic readiness. Tailored interventions, such as breaking down tasks into manageable steps, significantly boost engagement and prevent misbehavior stemming from boredom or frustration.
Ultimately, effective staff training, ongoing administrative support, and constructive collaboration between educators and behavior analysts contribute to the successful implementation of ABA strategies, leading to a more focused and supportive educational environment.
Conclusion
As educators continue to seek effective solutions for managing disruptive behaviors in classrooms, school-based ABA therapy offers a proven approach that balances the needs of students and enhances their educational journeys. By focusing on individualized student needs, employing evidence-based strategies, and ensuring ongoing professional development, this therapy not only addresses challenges but paves the way for academic and social successes. The commitment to understanding and transforming classroom behaviors through ABA remains a crucial element in fostering positive educational outcomes for all students.
References
- School-Based ABA Therapy: Boosting Learning and Behavior
- 9 Proactive ABA Methods to Redirect Student Behavior
- How to Use ABA in the Classroom
- School-based ABA Therapy in Colorado
- Board certified behavior analysts and school fidelity of Applied ...
- Disruptive Behavior in the Classroom? Identifying the Cause Could ...
- How ABA Therapy Prepares Children for School Success
Find More Articles
Contact us
North Carolina, Tennessee, Nevada, New Jersey, Utah, Virginia
New Hampshire, Maine
Massachusetts, Indiana, Arizona, Georgia
.avif)











.jpeg)









































.jpeg)







.jpeg)
.jpeg)


.jpeg)















.jpeg)
.jpeg)



.jpeg)
.jpeg)






