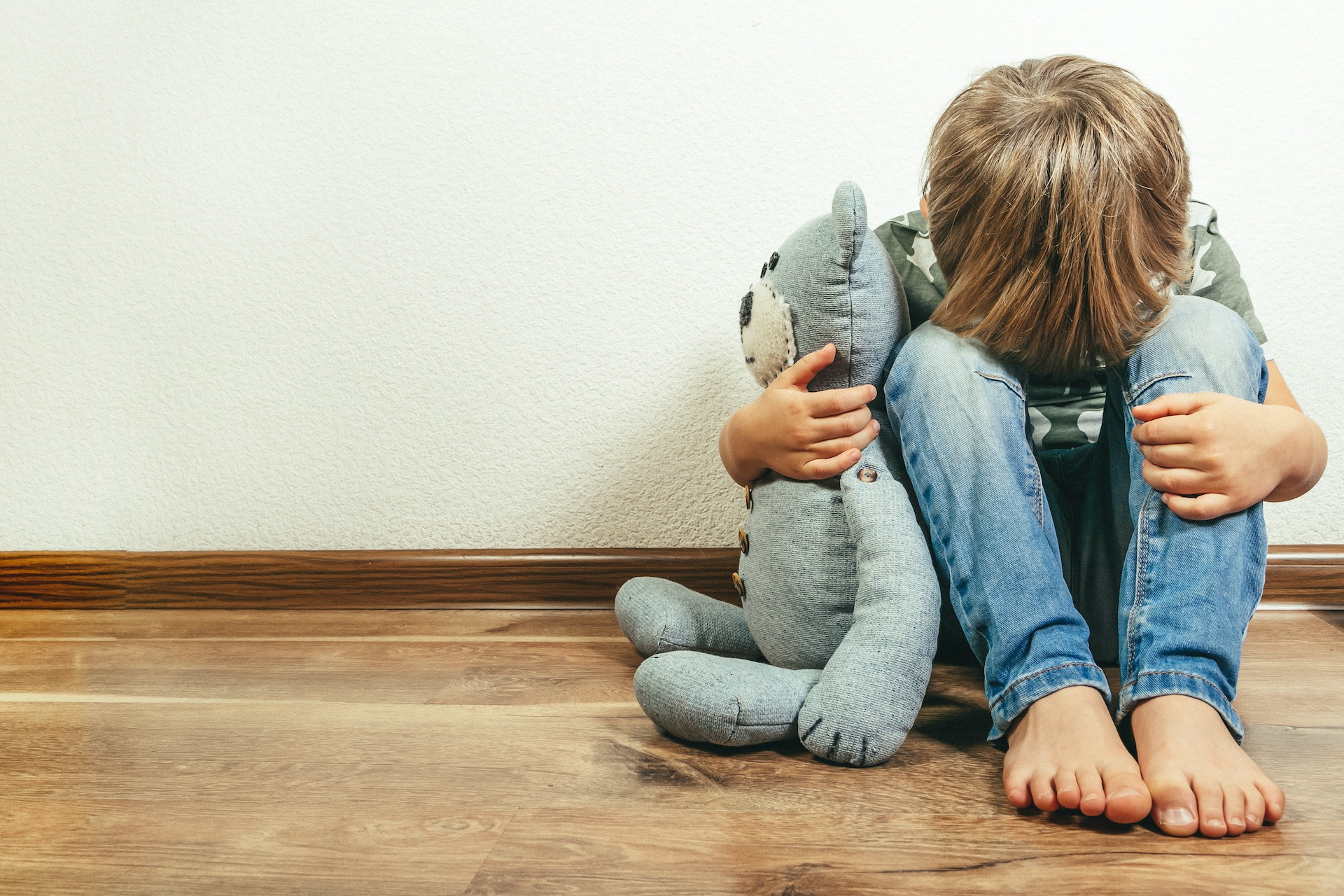
Can Autism Get Worse With Stress?
Delve into the nuanced relationship between stress and autism, understanding how heightened stress levels might impact individuals on the spectrum. Uncover insights with a compassionate perspective, recognizing the unique experiences of each person.

The Relationship Between Stress and Autism
Stress can have a significant impact on individuals with autism, potentially exacerbating their symptoms and affecting their overall well-being. Understanding the relationship between stress and autism is crucial for effectively supporting individuals on the autism spectrum. In this section, we will explore the impact of stress on autism symptoms and delve into the stress response in autism.
The Impact of Stress on Autism Symptoms
Stress can influence various aspects of autism symptoms, potentially making them more pronounced or challenging to manage. Increased stress levels can lead to heightened anxiety and emotional regulation difficulties in individuals with autism. They may experience difficulty managing their emotions, becoming overwhelmed by even minor triggers or changes in their environment. This can manifest as increased irritability, meltdowns, or withdrawal from social interactions.
Additionally, stress can aggravate sensory issues commonly experienced by individuals with autism. Sensory overload and sensitivity can become more pronounced under stressful conditions, making it even more challenging for individuals to process and integrate sensory information. This can lead to sensory meltdowns or a heightened aversion to certain sensory stimuli.
Furthermore, stress can impact executive functioning and cognitive abilities in individuals with autism. Executive functions, such as planning, problem-solving, and decision-making, can be adversely affected by stress. This can lead to difficulties in managing daily tasks, adapting to changes, and maintaining cognitive flexibility.

Understanding the Stress Response in Autism
The stress response in individuals with autism may differ from that of neurotypical individuals. Individuals on the autism spectrum may have unique stress triggers and exhibit stress-related behaviors that are specific to their condition. Identifying these triggers and understanding the stress response can help caregivers and individuals with autism develop effective coping strategies.
Stress triggers in autism can vary widely among individuals. Certain situations or stimuli that may not typically be considered stressful can trigger stress responses in individuals with autism. For example, a change in routine or unexpected events can cause significant distress.
Understanding the unique stress response in autism can enable caregivers to provide appropriate support and intervention. By recognizing the signs of stress, caregivers can implement strategies to help individuals with autism manage their stress levels effectively.
By recognizing the impact of stress on autism symptoms and understanding the stress response in autism, caregivers and individuals with autism can work together to implement strategies that promote well-being and enhance quality of life.
Factors that Contribute to Stress in Autism
Individuals with autism often face unique challenges that can lead to increased stress levels. Understanding the factors that contribute to stress in autism is essential for providing appropriate support and intervention. Three key factors that commonly contribute to stress in individuals with autism are sensory overload and sensitivity, social interactions and communication challenges, and changes in routine and unexpected events.
Sensory Overload and Sensitivity
Sensory overload occurs when an individual with autism is exposed to an overwhelming amount of sensory stimuli. The sensory system of individuals with autism may be hypersensitive or hyposensitive, causing them to experience sensory information differently than neurotypical individuals. This heightened sensitivity can lead to distressing and overwhelming situations, triggering stress responses.
Sensory Overload Triggers and Impact on Stress
- Loud noises: Increased anxiety and agitation.
- Bright lights: Visual discomfort and sensory overwhelm.
- Strong smells: Disruption of focus and concentration.
- Tactile sensations: Physical discomfort and sensory overload.
To help individuals with autism manage sensory overload, it is important to create a sensory-friendly environment that minimizes overwhelming stimuli. This may include providing quiet spaces, using dimmed lighting, and offering sensory tools such as weighted blankets or noise-cancelling headphones.
Social Interactions and Communication Challenges
Social interactions and communication can be particularly challenging for individuals with autism. Difficulties in understanding nonverbal cues, maintaining eye contact, and engaging in reciprocal conversation can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration. These challenges can contribute to increased stress levels, as individuals with autism may struggle to navigate social situations successfully.
Social Interaction and Communication Challenges and Impact on Stress
- Difficulty understanding social cues: Feeling confused or misunderstood.
- Challenges with initiating or maintaining conversations: Frustration and social anxiety.
- Sensory overload in social settings: Overwhelm and withdrawal.
- Difficulty expressing needs and emotions: Increased stress and frustration.
Supporting individuals with autism in social interactions involves providing clear and explicit communication, incorporating visual supports, and offering social skills training. By addressing these challenges, individuals with autism can develop coping strategies and reduce stress related to social interactions.
Changes in Routine and Unexpected Events
Individuals with autism often thrive on predictability and routine. Changes in routine or unexpected events can disrupt their sense of stability and control, leading to increased stress levels. Even minor changes, such as a different schedule or an unexpected disruption, can be overwhelming for individuals with autism.
Changes in Routine and Unexpected Events and Impact on Stress
- Schedule changes: Heightened anxiety and resistance.
- Unfamiliar environments: Discomfort and unease.
- Unexpected transitions: Increased stress and meltdowns.
- Interruptions to preferred activities: Frustration and emotional dysregulation.
Establishing clear and predictable routines can help individuals with autism feel more secure and reduce stress. Visual schedules, advance notice of changes, and providing support during transitions can also contribute to a smoother adjustment to new situations.
By understanding the factors that contribute to stress in autism, caregivers, educators, and professionals can implement strategies to support individuals with autism in managing stress and promoting overall well-being. Through tailored interventions and a supportive environment, it is possible to mitigate stress and enhance the quality of life for individuals with autism.
How Stress can Worsen Autism Symptoms
Stress can have a significant impact on individuals with autism, potentially exacerbating their symptoms and challenges. Understanding how stress can worsen autism symptoms is crucial for developing effective strategies to support individuals on the autism spectrum.
Increased Anxiety and Emotional Regulation Difficulties
One way in which stress can worsen autism symptoms is by increasing anxiety levels and exacerbating difficulties with emotional regulation. Individuals with autism often experience higher levels of anxiety compared to neurotypical individuals. Stressful situations can amplify this anxiety, making it more challenging for individuals with autism to manage their emotions effectively.
Heightened anxiety can manifest in various ways, including increased restlessness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It may also lead to heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli, making it harder for individuals with autism to filter out background noises, lights, or other sensory inputs.
Aggravated Sensory Issues and Meltdowns
Stress can also aggravate sensory issues in individuals with autism, potentially leading to meltdowns or other stress-related behaviors. Many individuals with autism have sensory sensitivities, making them more susceptible to feeling overwhelmed by certain stimuli. When faced with stressful situations, these sensory sensitivities can become heightened, making it even more challenging for individuals with autism to cope.
For example, a crowded and noisy environment that might already be overwhelming for someone with autism can become even more distressing under stress. This can trigger meltdowns, which are intense reactions to sensory overload and emotional overwhelm.
Impaired Executive Functioning and Cognitive Abilities
Stress can also impact executive functioning and cognitive abilities in individuals with autism. Executive functioning refers to a set of skills that help individuals plan, organize, and regulate their behavior. When under stress, individuals with autism may experience difficulties with these executive functions, leading to challenges in decision-making, problem-solving, and impulse control.
Stress can impair working memory, making it harder for individuals with autism to retain and process information effectively. This can further hinder their ability to adapt to new or unexpected situations, as well as manage tasks that require multitasking or flexible thinking.
Understanding how stress can worsen autism symptoms is crucial for caregivers and individuals with autism themselves. By recognizing the impact of stress on anxiety levels, sensory sensitivities, and cognitive abilities, strategies can be implemented to mitigate the negative effects of stress. These strategies can include creating a calming environment, teaching coping strategies, establishing predictable routines, and providing clear communication.
Managing Stress for Individuals with Autism
For individuals with autism, managing stress is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and minimizing the impact of stress on autism symptoms. By implementing strategies to create a calming environment, teaching coping strategies and emotional regulation techniques, and establishing predictable routines with clear communication, individuals with autism can better navigate stressors and mitigate their effects.
Creating a Calming Environment
Creating a calming environment is essential for individuals with autism to reduce stress levels. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Sensory Considerations: Pay attention to sensory triggers that may cause stress and make modifications accordingly. This may involve providing a quiet space, using ear defenders or headphones to reduce noise, adjusting lighting, or offering sensory tools such as fidget toys or weighted blankets.
- Visual Supports: Visual supports, such as visual schedules or social stories, can provide predictability and help individuals understand what to expect, reducing anxiety and stress. Visual cues can also be used to communicate rules, expectations, and steps for various activities.
- Structured Spaces: Organize physical spaces to provide structure and minimize clutter. Clearly define areas for specific activities, ensuring that each space is organized and free from distractions that may contribute to stress.
Teaching Coping Strategies and Emotional Regulation Techniques
Equipping individuals with autism with coping strategies and emotional regulation techniques empowers them to manage stress and its impact on their well-being. Consider the following approaches:
- Deep Breathing and Relaxation Techniques: Teach deep breathing exercises and relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery, to help individuals calm their minds and bodies during stressful situations.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Introduce mindfulness and meditation practices tailored to individuals with autism. These practices can improve self-awareness, reduce anxiety, and enhance emotional regulation.
- Social and Communication Skills: Enhance social and communication skills to help individuals effectively express their emotions and seek support when needed. Teaching assertiveness and problem-solving techniques can empower individuals to cope with stressors in a constructive manner.
Establishing Predictable Routines and Clear Communication
Establishing predictable routines and maintaining clear communication are essential for individuals with autism. Predictability and clarity can reduce anxiety and stress by providing a sense of structure and understanding. Consider the following strategies:
- Consistent Daily Routine: Establish a consistent daily routine that incorporates regular mealtimes, sleep schedules, and activities. Clearly communicate the schedule using visual supports and verbal reminders to provide a predictable framework for the individual.
- Visual and Written Supports: Utilize visual supports, such as visual schedules, calendars, or checklists, to visually represent the daily routine, tasks, or upcoming events. Written supports, such as social stories, can help individuals understand and prepare for new or challenging situations.
- Clear and Concise Communication: Use clear and concise language when communicating with individuals with autism. Avoid vague or ambiguous instructions, and provide visual cues or gestures to support verbal communication when necessary.
By implementing these strategies, individuals with autism can effectively manage stress and reduce its impact on their overall well-being. Remember to tailor these approaches to meet the unique needs and preferences of each individual.
Support for Caregivers of Individuals with Autism
Caring for individuals with autism can be both rewarding and challenging. The stress associated with supporting and understanding the unique needs of someone with autism can take a toll on caregivers. It is essential for caregivers to prioritize their own well-being and seek support when needed. Here are some strategies that can help caregivers manage their stress and find the support they need.
Self-Care and Managing Caregiver Stress
Taking care of oneself is crucial for caregivers of individuals with autism. Managing caregiver stress is essential to maintain physical and emotional well-being. Here are some self-care strategies that can help caregivers navigate the demands of their role:
- Pursue personal interests: Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce stress. Whether it's reading a book, practicing a hobby, or spending time in nature, finding time for oneself is important.
- Practice self-care routines: Prioritizing self-care routines, such as getting enough sleep, eating nutritious meals, and exercising regularly, can help caregivers maintain their physical and mental well-being.
- Seek respite: Taking regular breaks from caregiving responsibilities is crucial. Caregivers can seek respite care services or enlist the help of family and friends to provide temporary relief.
Seeking Professional Help and Support Networks
Caregivers of individuals with autism should not hesitate to seek professional help and tap into support networks. Here are some avenues for finding support:
- Therapy or counseling: Engaging in therapy or counseling sessions can provide caregivers with a safe space to express their feelings, learn coping strategies, and gain valuable insights into managing stress.
- Support groups: Joining support groups specifically tailored for caregivers of individuals with autism can provide a sense of community and understanding. These groups offer an opportunity to share experiences, exchange information, and receive support from others who are going through similar challenges.
- Online resources: Online forums, blogs, and websites dedicated to autism and caregiving can be valuable sources of information and support. Caregivers can connect with others, access helpful resources, and gain insights from experts in the field.
Building a Strong Support System
Building a strong support system is crucial for caregivers of individuals with autism. Here are some ways caregivers can create a network of support:
- Family and friends: Building a support system that includes family members and friends can provide caregivers with emotional support, practical assistance, and respite care.
- Professional networks: Connecting with professionals, such as therapists, educators, or medical practitioners, who specialize in autism can offer valuable guidance and support.
- Community organizations: Engaging with community organizations that focus on autism can provide caregivers with access to resources, workshops, and events that promote education, advocacy, and support.
Remember, caregivers play a vital role in the lives of individuals with autism, and taking care of themselves is essential to provide the best support possible. By prioritizing self-care, seeking professional help when needed, and building a strong support system, caregivers can better manage their stress and find the support they require.
Summary
In wrapping up our discussion on whether stress can worsen autism, it's clear that emotions play a significant role in the well-being of individuals on the autism spectrum. While stress itself may not directly cause autism, it's evident that it can exacerbate certain challenges for those already navigating the complexities of the spectrum.
Understanding and managing stress levels is crucial for individuals with autism, as heightened stress may amplify sensory sensitivities and communication difficulties. As a community, it's important to approach this topic with empathy and support, recognizing the unique needs and experiences of each person.
Promoting environments that foster understanding, providing effective coping mechanisms, and encouraging open communication can make a positive impact. By acknowledging the impact of stress on individuals with autism and working collectively to create supportive spaces, we can contribute to a more inclusive and compassionate world for everyone.
Sources
Find More Articles
Contact us
North Carolina, Tennessee, Nevada, New Jersey, Utah, Virginia
New Hampshire, Maine
Massachusetts, Indiana, Arizona, Georgia
.avif)